Crop signals
Bacteria engineered to detect pollution or nutrients could help farmers monitor their fields.
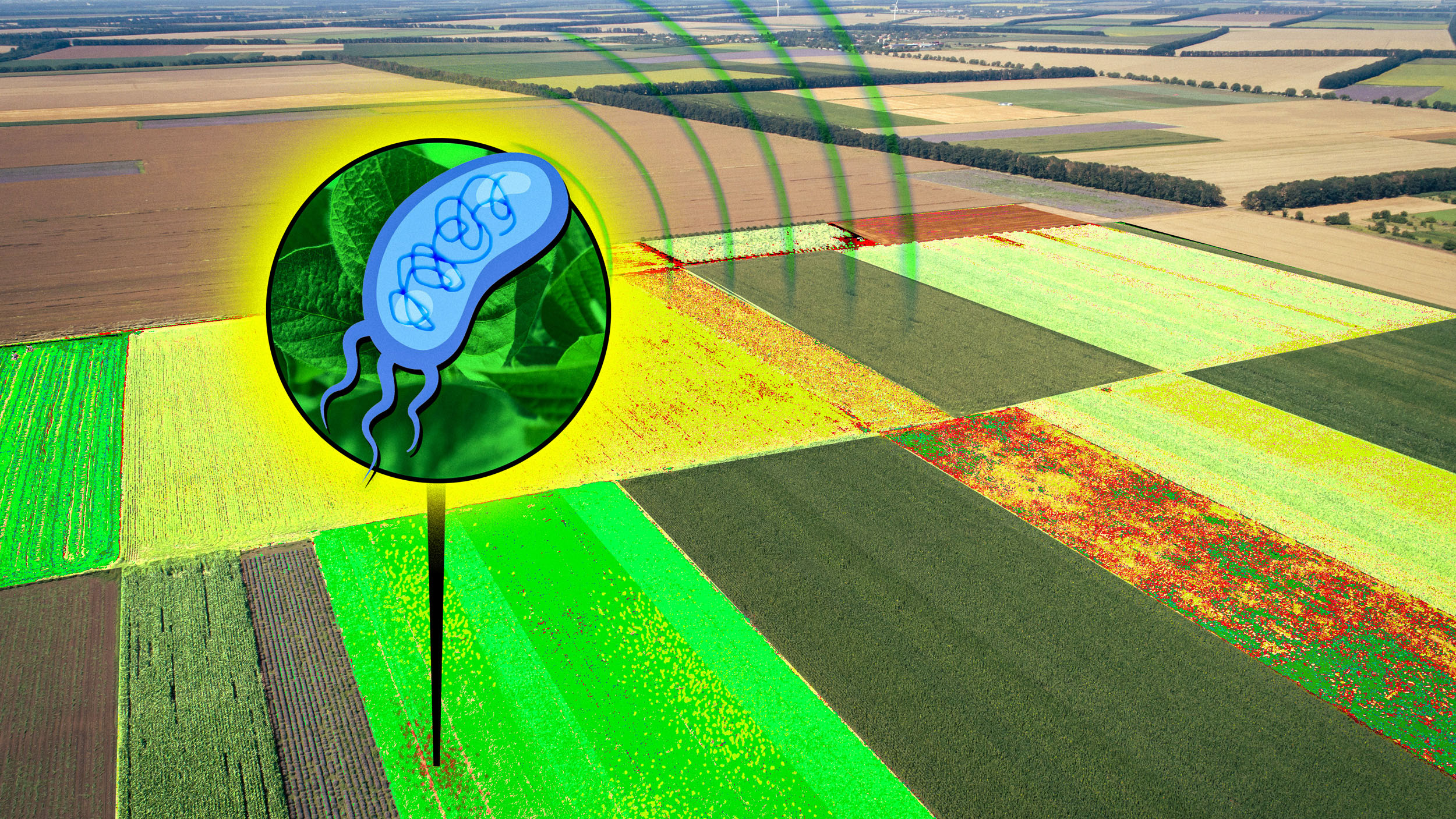
Bacteria can be engineered to sense a variety of molecules, such as pollutants or soil nutrients, but usually these signals must be detected microscopically. Now Christopher Voigt, head of MIT’s Department of Biological Engineering, and colleagues have triggered bacterial cells to produce signals that can be read from as far as 90 meters away. Their work could lead to the development of sensors for agricultural and other applications, which could be monitored by drones or satellites.
The researchers engineered two different types of bacteria, one found in soil and one in water, so that when they encounter certain target chemicals, they produce hyperspectral reporters—molecules that absorb distinctive wavelengths of light across the visible and infrared spectra. These signatures can be detected with hyperspectral cameras, which determine how much of each color wavelength is present in any given pixel. Though the reporting molecules they developed were linked to genetic circuits that detect nearby bacteria, this approach could also be combined with sensors detecting radiation, soil nutrients, or arsenic and other contaminants.
“The nice thing about this technology is that you can plug and play whichever sensor you want,” says Yonatan Chemla, an MIT postdoc who is a lead author of a paper on the work along with Itai Levin, PhD ’24. “There is no reason that any sensor would not be compatible with this technology.” The work is being commercialized through Fieldstone Bio.
Keep Reading
Most Popular
We did the math on AI’s energy footprint. Here’s the story you haven’t heard.
The emissions from individual AI text, image, and video queries seem small—until you add up what the industry isn’t tracking and consider where it’s heading next.
We’re learning more about what weight-loss drugs do to the body
GLP-1 agonists like Wegovy, Ozempic, and Mounjaro might benefit heart and brain health—but research suggests they might also cause pregnancy complications and harm some users.
This giant microwave may change the future of war
The defense tech startup Epirus has developed a cutting-edge, cost-efficient drone zapper that’s sparking the interest of the US military. Now the company has to deliver.
How a new type of AI is helping police skirt facial recognition bans
Adoption of the tech has civil liberties advocates alarmed, especially as the government vows to expand surveillance of protesters and students.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from
MIT Technology Review
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.